
- Home
- Media Center
-
Events
- Wuzhen Summit
- Regional Forums
- Practice Cases of Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- The Light of Internet Expo
- Straight to Wuzhen Competition
- Global Youth Leadership Program
- WIC Distinguished Contribution Award
- Membership
- Research & Cooperation
- Digital Academy
-
Reports
- Collection of cases on Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- Collection of Shortlisted Achievements of World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- Reports on Artificial Intelligence
- Reports on Cross—Border E—Commerce
- Reports on Data
- Outcomes of Think Tank Cooperation Program
- Series on Sovereignty in Cyberspace Theory and Practice
- Other Achievements
- About WIC
- 中文 | EN

Collection: Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace (Based on KasperskyOS)
Kaspersky Centerm (TONK in Russia) provides hardware platform, technical and expert support.
Cyberattacks and malware deployments are common targets on enterprise workstations. To reduce the risk of attack, thin clients can be used instead of traditional personal computers. In order to reduce this risk to a minimum, KasperskyOS built a secure-by-design solution based on thin client hardware.
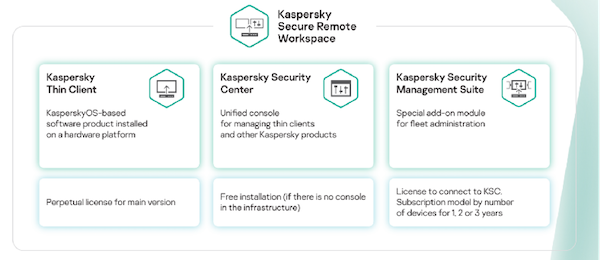
"Kaspersky Cyber Immunity" Design Lays the Foundation for the Strong Performance of the Product
Kaspersky Cyber Immunity - a unique combination of ideology, methodology, secure architecture, and Kaspersky OS (the microkernel was developed from scratch by Kaspersky) enables secure-by-design thin client infrastructure.
Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace is a combination of the following features:
The Kaspersky Thin Client (KTS) is an endpoint security solution that is installed on the TONK TN1200 hardware platform, which significantly enhances the security of endpoints.
An enterprise-grade management console for Kaspersky products, Kaspersky Security Center (KSC).
Furthermore, Kaspersky Security Management Suite (KSMS) enables centralized management of thin client infrastructure as an add-on module for Kaspersky Security Center.
This helps management of up to 100000 nodes from one center: monitoring, configuring, and delivering updates for all thin clients. When connected to the Kaspersky remote workspace infrastructure, the thin client end performs automatic software deployment, vulnerability assessment, patching, registration, and configuration.
With Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace, one of the most innovative achievements has been the improvement of endpoint security to previously unreasonably high levels, as well as the enhancement of IT endpoint lifecycle management, such as deployment, configuration, inventory management, and patch/update management.

More than 100 Pilot Projects Proved a Good Basis for Promotion
Using Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace can be beneficial in many situations that involve a large number of workstations that perform similar tasks and use a standard set of applications. For example:
- Public Sector
- Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI)
- Healthcare
- Education
- Industrial Automation
- Energy, Gas and Oil
- Retail
Customers and partners have been able to use Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace since the beginning of 2022. Over 100 pilot projects have been completed for clients by the team. For public organizations and university institutions, which have already implemented cyber-resistant thin client infrastructure projects.
Kaspersky intends to deliver the solution to markets where it has already established a presence in 2023. Kaspersky products are used in more than 200 countries and territories.
Innovative technology enabled cost savings
According to Kaspersky's research, using Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace can reduce an organization's total cost of ownership by at least 20% as compared with using classical desktops, laptops, and nettops based on other operating systems. Furthermore, the Kaspersky Thin Client is a device that is already secure by design with the same level of performance as other solutions.
By optimizing workplace costs, companies are able to improve their employees' social environments.
Patents and Products Stimulate the Development of the Industry
Kaspersky Secure Remote Workspace has received five Chinese national patents to date. As a company, Kaspersky believes that Cyber Immunity is the future of IT and information security. Currently, Kaspersky is ahead of its competitors when it comes to developing immune solutions. Although Kaspersky holds the leading position in this field, other companies are also required to develop similar solutions. In order to inspire other companies, Kaspersky have released commercial Cyber Immune products, which are currently available on the market.

The World Internet Conference (WIC) was established as an international organization on July 12, 2022, headquartered in Beijing, China. It was jointly initiated by Global System for Mobile Communication Association (GSMA), National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China (CNCERT), China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), Alibaba Group, Tencent, and Zhijiang Lab.





