
- Home
- Media Center
-
Events
- Wuzhen Summit
- Regional Forums
- Practice Cases of Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- The Light of Internet Expo
- Straight to Wuzhen Competition
- Global Youth Leadership Program
- WIC Distinguished Contribution Award
- Membership
- Research & Cooperation
- Digital Academy
-
Reports
- Collection of cases on Jointly Building a Community with a Shared Future in Cyberspace
- Collection of Shortlisted Achievements of World Internet Conference Awards for Pioneering Science and Technology
- Reports on Artificial Intelligence
- Reports on Cross—Border E—Commerce
- Reports on Data
- Outcomes of Think Tank Cooperation Program
- Series on Sovereignty in Cyberspace Theory and Practice
- Other Achievements
- About WIC
- 中文 | EN

China leads the way in building a community with a shared future in cyberspace in the field of microbiology
China leads the way, with 141 institutions from 51 countries, in mapping out a global solution for the interconnection of microbiological big data infrastructure and a community with a shared future in cyberspace in the field of microbiology, thereby promoting global open science, economic development and industrial progress.
Working together to construct a global big data platform for microbial resources and a global cooperation network to enhance global economic development and industrial progress
By the supports of China National Microbiology Data Center (NMDC), CAS Microbiology Data Center, Information Center of CAS Bio-Resource Project, China Network for Science and Technology (CSTNET), WFCC-MIRCEN World Data Center for Microorganisms (WDCM), CAS Sustainable Development Dig Data Platform System, The Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences adheres to the "China-Orientation" international cooperation basing on China Science and Technology Network (CSTNET), effectively use blockchain technology, bioinformation technology, cloud service platforms and supercomputer resources, establishes a Global Microbial Data Informatization Cooperation Network with 141 partners from 51 countries, takes the lead in the establishment of the Global Catalogue of Microorganisms, promotes the construction of global microbial informatization to a new height, and effectively promotes the effective utilization of the global microbial data resources.

WDCM Global Cooperation Nodes System
Microbial resources, fundamental to the ecosystem, is a basic source of human production and life, an important material basis for human survival, a cornerstone for biotechnology and industrial development, as well as a crucial strategic resource to ensure national food security, ecological security and energy security. The collection, conservation, protection, development and utilisation of biological resources wields an influence in guaranteeing people's health and supporting the sustainable development of the national economy. The catalogue of microbial resources provides scientists and industrial users with a single effective point of access to microbial resources from microbial resources preservation institutes of countries concerned. Collectively, the global catalogue of microbial resources offers users a one-stop access to global physical information of microbial resources and optimizes the construction of global microbial informatization to a new altitude, and thus promote the effective utilization of global microbial resources.
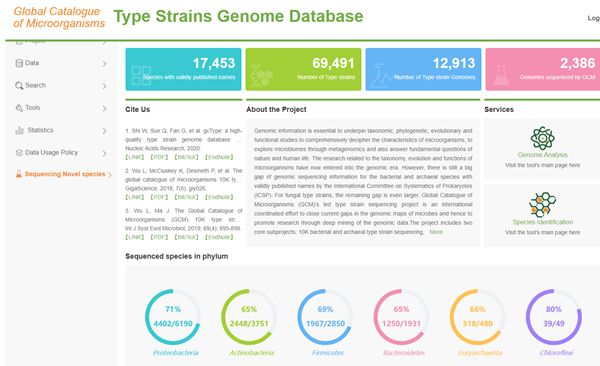
Web site of WDCM 10K Type Strain Sequencing Project
Leading the sequencing project of tens of thousands of microbial standard strains to promote global open science in microbiology
Type strains are preserved as pure strains in the microbial nomenclature, microbial taxonomy and record as well as publication, which serve as reference material in microbial taxonomic studies and ideal tools for biotechnological research, endowed with high value in scientific researches and industry. The Bureau of International Cooperation of Chinese Academy of Sciences arranged The global cooperation plan for genome sequencing, data mining and functional analysis of model microorganisms. By the supports of this plan, The global sequencing project of tens of thousands of microbial type strains led by our center has been officially joined by 26 microbial resources preservation institutes from 12 countries, including the United States, Russia, Japan, South Korea, the Netherlands, Portugal, Sweden, Thailand, etc. The project renders us a mechanism and platform for effective integration of type microbial resources worldwide and realizes efficient inventory of type microbial resources, thereby promoting the development of microbial taxonomy. On the premise that the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) aims to protect the interests of resource-exporting countries, this project accelerates the sharing and utilization of microbial resources, which is as well the embodiment of Chinese wisdom and solutions to international cooperation in compliance with the CBD and the transnational transfer of biological resources and benefit-sharing mechanisms under the Nagoya Protocol.
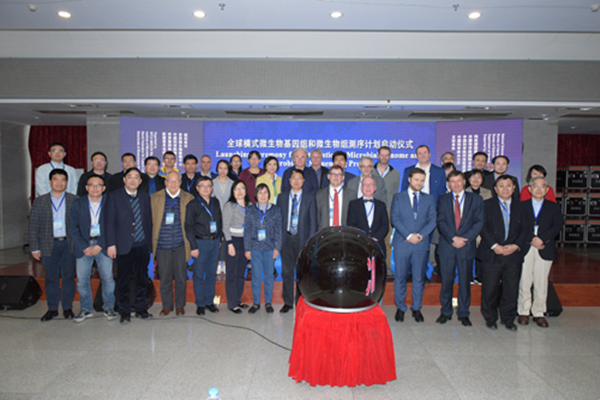

The Ceremony of WDCM 10K Type Strain Sequencing Project
Establishing ISO standard for data to optimize global high-quality infrastructure for microorganisms and realize global interconnection
Data standards are the basis of global data sharing, the key to improve data quality, and the premise of the establishment of an international first-class database. National Microbiology Data Center of Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and National Science & Technology Infrastructure Platform Center, et al. combine with nine countries including the United States, Japan, Russia, South Korea and other countries, and formulate the first ISO-level data standard of ISO 21710:2020 Biotechnology in the international microbial field, laying a solid foundation for global data sharing, based on which they established internationally significant databases including Global Catalogue of Type Strain, gcType and The Global Catalogue of Metagenomics, gcMeta, providing the key infrastructure for microbial field research.

WDCM Global Training Courses, Symposiums and ISO Standard Development
By virtue of the sound base provided by established databases, the team has made full use of artificial intelligence-based machine learning model and semantic network technology to conduct thorough study of massive biological data, and established Analyzer of Bio-Resources Citation, pathogenic microbial knowledge atlas and other models and systems. Global microbial resources, omics, literature, patents and other data in microbiology field from 1953 to now were studied by this team to realize monitoring and tracking of all the information in each link of the microbial resources collection, preservation, transnational transfer, academic and commercial applications and benefit sharing, which provides a solid objective data support for the utilization of biological resources and biodiversity protection.

Video Message from the Executive Secretary of the Convention on Biological Diversity

The World Internet Conference (WIC) was established as an international organization on July 12, 2022, headquartered in Beijing, China. It was jointly initiated by Global System for Mobile Communication Association (GSMA), National Computer Network Emergency Response Technical Team/Coordination Center of China (CNCERT), China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), Alibaba Group, Tencent, and Zhijiang Lab.





